Presenter: Yikai Hsieh (Assistant Professor, RISH, Kyoto University)
Title: Earth’s radiation belts dynamics associated with parallel and obliquely propagating whistler-mode chorus emissions
Place: Online
Associated Mission: Mission 3 (Sustainable Space Environments for Humankind)
If you would like to participate, please e-mail me your name, affiliation and e-mail address by 10 am on the day.
(Open Seminar Office: openseminar@rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp)
Abstract
Radiation belts surrounding the Earth are regions filled with energetic electrons and ions. Relativistic electrons (energy ~ MeV) inside the radiation belt can damage spacecraft and space shuttles carrying astronauts. Understanding the formation and loss processes is an important issue nowadays. Energetic electron accelerations and precipitations in the outer radiation belt are highly associated with wave-particle interactions between electrons and whistler-mode chorus emissions. Two main processes take place in the whistler-mode wave-particle interactions. One is the nonlinear scattering process, which makes electron energy slightly smaller. The other is the nonlinear trapping process, which makes effective energy gain of resonant electrons. We perform test particle simulations in a 3D dipole field to reproduce the interactions between parallel and obliquely propagating chorus and electrons in the radiation belt. The formation and loss processes of the outer radiation belt electrons are verified by tracing interactions with consecutive emissions. In the formation process, MeV electrons are generated promptly within a few seconds due to the nonlinear trapping of cyclotron resonance and Landau resonance of oblique chorus waves. In the loss process, we find that the nonlinear scattering via cyclotron resonance is the primary process that pushes energetic electrons into the loss cone in both parallel and oblique cases. The obliquely propagating chorus causes more energetic electron precipitation than the parallel propagating chorus because of the combination of nonlinear trapping via Landau resonance and nonlinear scattering via cyclotron resonance.
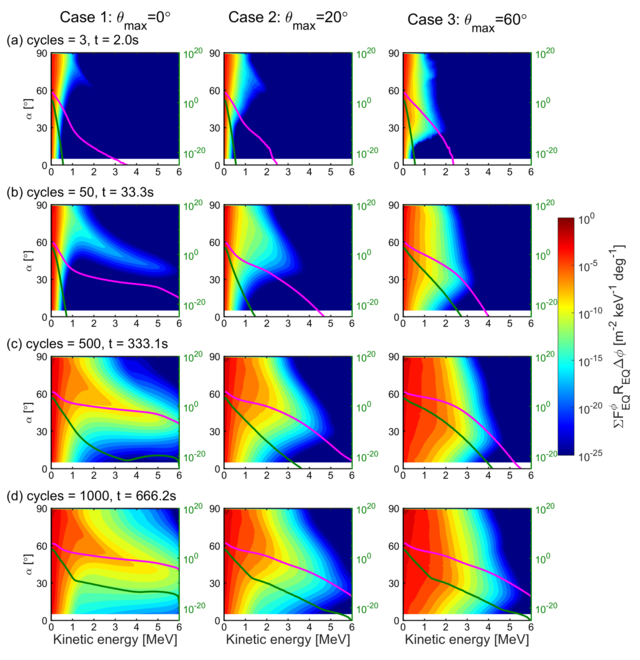 Figure 1: Electron acceleration (distribution at the high energy parts) and precipitation (dark green curves) after interacting with 3, 50, 500, and 1000 chorus emissions.
Figure 1: Electron acceleration (distribution at the high energy parts) and precipitation (dark green curves) after interacting with 3, 50, 500, and 1000 chorus emissions.
PDF (218 598 bytes) | Top
15 June, 2022


