
Overview
EAR is a large Doppler radar facility located at the equator in West Sumatra, Republic of Indonesia. It consists of 560 Yagi-antennas in a circular field of 110 m in diameter. EAR has almost the same functionality as the MU radar except that the output power is 100 kW. It can observe winds and turbulence in the altitude range of 1.5 km to 20 km (troposphere and lower-stratosphere), and ionospheric irregularities at an altitude above 90 km.
 Photo: Antenna field of the EAR
Photo: Antenna field of the EAR
In close collaboration with the National Institute for Aeronautics and Space (LAPAN) of Indonesia, EAR has carried out long-term observations since June 2001. Research funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research for Priority Areas “Coupling Processes in the Equatorial Atmosphere (CPEA)” is currently being conducted during 2001–2006 as a collaborative study involving Shimane University, Tokyo Metropolitan University and Nagoya University. During the course of the CPEA projcet, various instruments have been accumulated in the EAR site.
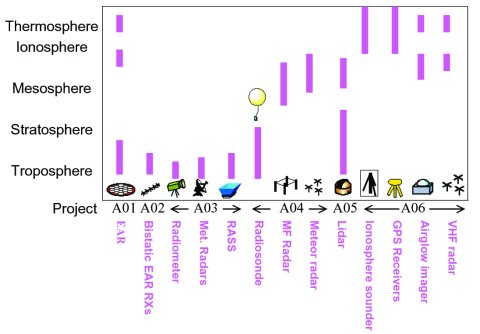 Figure: Various instrument in the EAR site
Figure: Various instrument in the EAR site
In addition to the EAR, we operate mediam frequency (MF) radar and boundary layer radar facilities in suburbs of Jakarta, West Kalimantan, South Jawa, which participate in a regional radar network in Indonesia, EAR, the MU radar and number of radar facilities in other countries forms international network of atmospheric radars around the equator.
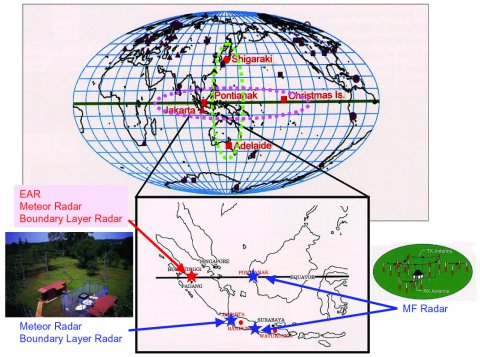 Figure: International network of atmospheric radars around the equator
Figure: International network of atmospheric radars around the equator
1072 × 797 JPEG file (236 048 Bytes)
Return to Top page | Department of Collaborative Research Programs.
|

